Placental Growth Factor in Beta-cellsplays an Essential Role in Gestational Beta-cell Growth
Yang W, Jiang Y, Wang Y, Zhang T, Liu Q, Wang C, Swisher G, Wu N, Chao C, Prasadan K, Gittes GK and Xiao X
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care
2020 Jan
Calpastatin Mediates Development of Alzheimer’s Disease in Diabetes
Zhu L, Gong L, Yang T, Xiao X
Journal of Alzheimers Disease
2019 Mar 19
Prion Protein is Essential for Diabetic Retinopathy-associated Neovascularization
Zhu L, Xu J, Liu Y, Gong T, Liu J, Huang Q, Fischbach S, Zou W, Xiao X
Angiogenesis
2018 May 30
Endogenous Reprogramming of Alpha Cells into Beta Cells Induced by Viral Gene Therapy Reverses Autoimmune Diabetes
Xiao X, Guo P, Shiota C, Zhang T, Coudriet GM, Fischbach S, Prasadan K, Fusco J, Ramachandran S, Witkowski P, Piganelli JD, Gittes GK
Cell Stem Cell
2018 Jan 6
SMAD3/Stat3 Signaling Mediates β-Cell Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Chronic Pancreatitis-Related Diabetes
Xiao X, Fischbach S, Zhang T, Chen C, Sheng Q, Zimmerman R, Patnaik S, Fusco J, Ming Y, Guo P, Shiota C, Prasadan K, Gangopadhyay N, Husain SZ, Dong H, Gittes GK
Diabetes
2017 Oct
Pancreatic Cell Tracing, Lineage-tagging, and Targeted Genetic Manipulations in Multiple Cell Types Using Pancreatic Ductal Infusion of Adeno-associated Viral Vectors and/or Cell-tagging Dyes
Xiao X, Guo P, Prasadan K, Shiota C, Peirish L, Fischbach S, Song Z, Gaffar I, Wiersch J, El-Gohary Y, Husain SZ, Gittes GK
Nature Protocols
2014 Oct 31
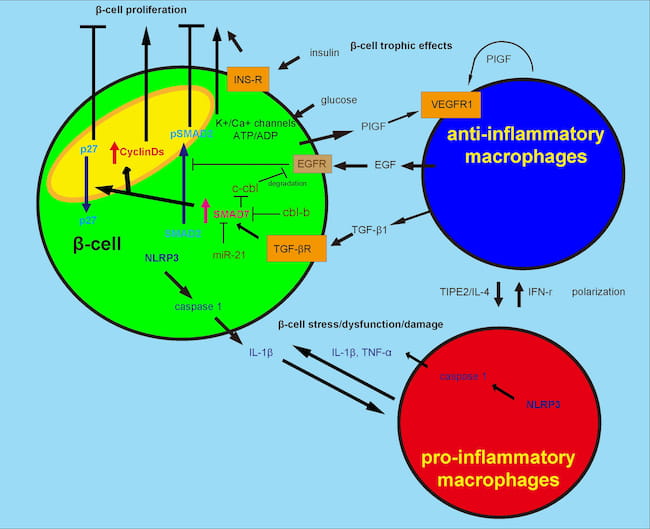
M2 Macrophages Promote Beta-cell Proliferation by Up-regulation of SMAD7
Xiao X, Gaffar I, Guo P, Wiersch J, Fischbach S, Peirish L, Song Z, El-Gohary Y, Prasadan K, Shiota C, Gittes GK
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA
2014 Mar 19
Pancreatic Duct Cells as a Source of VEGF in Mice
Xiao X, Prasadan K, Guo P, El-Gohary Y, Wiersch J, Gaffar I, Shiota C, Gittes GK
Diabetologia
2014 Feb 18
No Evidence for Beta Cell Neogenesis in Murine Adult Pancreas
Xiao X, Chen Z, Shiota C, Prasadan K, Guo P, El-Gohary Y, Paredes J, Welsh C, Wiersch J, Gittes GK
The Journal of Clinical Investigation
2013 Apr 27
TGFβ Receptor Signaling Is Essential for Inflammation-Induced but Not β-Cell Workload-Induced β-Cell Proliferation
Xiao X, Wiersch J, El-Gohary Y, Guo P, Prasadan K, Paredes J, Welsh C, Shiota C, Gittes GK
Diabetes
2013 Apr