- Find a Doctor
-
For Parents
- Before Your Visit
- During Your Visit
- After Your Visit
- More Resources for Parents
Patient & Visitor Resources -
Services
- Locations
-
About Us
- About Childrens
- Find it Fast
- Additional Resources
Find it FastAdditional Resources - MyCHP
ALERT:
There is construction in and around UPMC Children’s Hospital that is affecting the traffic flow – please allow for extra time traveling into the hospital.
- Find a Doctor
- For Parents
-
Services
-
Frequently Searched Services
- Asthma Center
- Brain Care Institute (Neurology & Neurosurgery)
- Cancer
- UPMC Children's Express Care
- Ear, Nose, & Throat (ENT)
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Gastroenterology
- Heart Institute
- Genetic & Genomic Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Nephrology
- Newborn Medicine
- Primary Care
- Pulmonary Medicine
- Rheumatology
- Surgery
- Transplant Programs
- See All Services
-
Frequently Searched Services
- Locations
- About Us
- MyCHP
- I Want To
- More Links









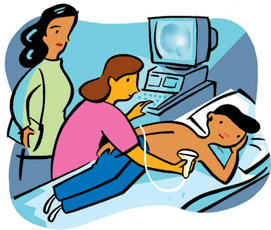 At
At  An echo may be done in a cardiology doctor’s office, in the hospital, or in one of the ambulatory care centers. You and your child will be taken into a small, darkened room. You may stay with your child during the entire test. Your child may hold a comfort item, and may watch or listen to a favorite video, during the test.
An echo may be done in a cardiology doctor’s office, in the hospital, or in one of the ambulatory care centers. You and your child will be taken into a small, darkened room. You may stay with your child during the entire test. Your child may hold a comfort item, and may watch or listen to a favorite video, during the test.
 If your child has any special needs or health issues you feel the doctor needs to know about, please call the Heart Institute at Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh before the test and ask to speak with a nurse. It is important to notify us in advance about any special needs your child might have.
If your child has any special needs or health issues you feel the doctor needs to know about, please call the Heart Institute at Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh before the test and ask to speak with a nurse. It is important to notify us in advance about any special needs your child might have.